Navigating Value-Based Pricing in SaaS: Strategies, Challenges, and Future Trends
Exploring Effective Strategies for Value-Based Pricing in the Dynamic SaaS Landscape.
Pricing a SaaS product can be challenging, but getting it right is extremely rewarding. In this article, we explore value-based pricing and its role in guiding B2B SaaS companies towards the effective application of key methodologies in their pricing process. We'll explore how setting prices based on customers perceived value can lead to better sales and more satisfied customers. We'll also discuss how AI is changing the way we think about pricing. This article is a straightforward guide to understanding and using value-based pricing in the SaaS industry.
Contents:
Introduction to Value-Based Pricing
The Three Core Aspects of Value Based Pricing Strategy
Understanding Unit Economics
Importance of Buyer Personas in Value Based Pricing
Quantifying a Buyer Persona
Determining the Right Value Metric
Identifying and Leveraging Value Metrics
Who should be on the Pricing Team?
Strategies for Implementing Value-Based Pricing
Case Studies
Common Challenges When Implementing Value-Based Pricing
The Future of Value-Based Pricing
The Role of AI in Augmenting Pricing Strategies
Introduction to Value-Based Pricing
In the context of SaaS business models, value-based pricing stands out as a strategic approach where prices are set based on the perceived value of the product or service by the customer, rather than on the cost of production or competitor prices. This model emphasizes understanding and leveraging the customer's perception of value, tailoring prices to reflect the benefits and outcomes that the product provides. In contrast to cost-plus or competitor-based strategies, value-based pricing focuses on customer-centric valuation, aligning pricing more closely with the unique benefits and features offered by the service.
This approach is particularly significant in the SaaS industry, where the intangible nature of software services and the ongoing customer relationship can make traditional pricing strategies less effective.
Value-based pricing in SaaS thus becomes a key tool for enhancing customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately driving growth and profitability.
In contrast, cost-plus focuses on covering costs and ensuring a profit margin, while competitor-based pricing aligns with market rates, potentially neglecting the product's unique value.
Pricing is crucial for every part of your business, yet it's often overlooked. This is because it intersects with multiple areas — marketing, sales, and product development — without being the main responsibility of any single team. This can lead to a disconnect in how a business approaches the market. But, when done right, as seen with companies like Freshworks, pricing can showcase your product's value clearly to different types of customers, making it clear why each feature is worth their investment.
The Three Core Aspects of Value Based pricing Strategy
In exploring the dynamics of Value-Based Pricing Strategy, we delve into its three core aspects: Positioning, Packaging, and Pricing. Each element plays a pivotal role in creating a pricing strategy that not only aligns with the perceived value of the product or service but also resonates with the target customer segment. Let's unpack these integral components to understand how they collectively contribute to a successful value-based approach in pricing.
The Freshworks’ pricing page illustrates a strategic approach to SaaS pricing, encapsulating these three pivotal elements:
1. Positioning: The service is positioned to appeal to a broad spectrum of customers, from small businesses to large enterprises. This is done by offering a range of packages that cater to different customer needs, ensuring that there is a suitable option for businesses of all sizes and types.
2. Packaging: The packaging of features within each tier is designed to allow companies to start with a basic set of features and scale up as their business grows. It ensures that businesses only pay for the features they need at each stage of their growth, with the option to expand their usage over time.
3. Pricing: Freshworks offers tiered pricing levels to accommodate the varied needs of their customers. Each tier is priced to match the value it provides, with higher tiers offering more advanced features and capabilities, aligning the price points with the added value and customers’ willingness to pay.
The pricing structure on the Freshworks page is designed to naturally guide users through an improved set of features as their needs grow. Starting with a free plan that suits small-scale users, there's a clear path to upgrade as their requirements expand. The balance between the different aspects—positioning, packaging, and pricing—is finely tuned, reflecting a strategic harmony essential for success. The top-tier plan remains flexible, accommodating larger customers who exceed the standard offerings. This highlights the pricing page's crucial role: it's where all paths converge, encapsulating your product's market fit, feature diversity, and cost—ultimately prompting the customer to make a purchase decision.
Understanding Unit Economics
Unit economics is a fundamental concept in pricing that focuses on the profitability of an individual unit sold by a company. It's especially crucial in the context of SaaS businesses where the 'unit' could be a subscription or a customer account. Understanding unit economics involves calculating the Lifetime Value (LTV) and the Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC).
In pricing strategy, the goal is to have a high LTV to CAC ratio, indicating that the revenue generated from a customer far exceeds the cost of acquiring them. A healthy SaaS business model typically aims for an LTV to CAC ratio of 3:1 or higher, ensuring sustainable growth and profitability.
Examples:
Let's consider a hypothetical SaaS company to understand the concepts of Lifetime Value (LTV) and Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) with some example numbers:
Example 1 - Basic SaaS Product: In this example, the LTV to CAC ratio is 2.4. This means that for every dollar spent on acquiring a new customer, the company earns $2.40 back over the customer's lifespan.
Example 2 - Advanced SaaS Product: The LTV to CAC ratio has increased to 3.6, indicating a more profitable scenario for the company with the advanced product.
Example 3 - Enterprise SaaS Product: The LTV to CAC ratio is now 2.4. Although the ratio is similar to the basic product scenario, the actual revenue and profit per customer are substantially higher.
These simplified examples illustrate how SaaS companies calculate and use LTV and CAC to assess the profitability of their pricing models and inform their marketing and product development strategies.
Importance of Buyer Personas in Value Based Pricing
A persona is a detailed, semi-fictional representation of your ideal customer based on market research and real data about your existing customers.
Personas help businesses understand their customers' needs, experiences, behaviors, and goals. In value-based pricing, personas are crucial as they enable you to tailor your pricing strategy to different segments of your target market. By understanding the specific characteristics and preferences of each persona, you can more effectively align your pricing with what each customer segment values most, leading to better customer satisfaction and improved business outcomes.
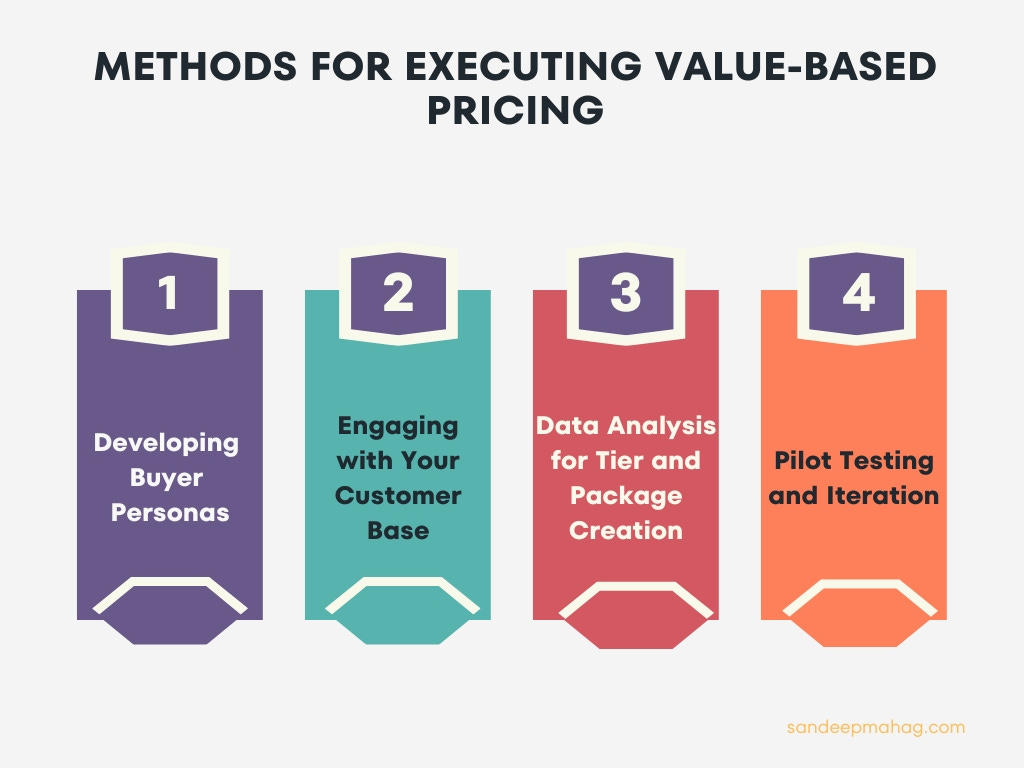
Methods for Calculating and Executing Value-Based Pricing
Calculating and implementing value-based pricing in your SaaS business is a data-intensive process, requiring detailed insights into your customers' needs and preferences. Here's are the steps involved:
Developing Buyer Personas:
Create detailed buyer personas representing your ideal customers. These personas should encompass various customer types, considering their backgrounds, roles, challenges, and what they seek from your product. Treat these personas as real individuals in strategy discussions to ensure your product and pricing align with their needs.
Engaging with Your Customer Base:
Gather both qualitative and quantitative data from your customers. Use surveys to understand how much they value different features and benefits, and what they are willing to pay. Target these surveys specifically at your buyer personas to ensure relevant and high-quality data. Keep these surveys concise and respectful of your customers' time.
Data Analysis for Tier and Package Creation:
Utilize the collected data to identify patterns and preferences among your buyer personas. Based on these insights, develop tiered pricing and bundled packages. This approach caters to a broader audience and opens opportunities for upselling. Ensure that each tier or package reflects the value perceived by different segments of your customer base.
Pilot Testing and Iteration:
Implement a trial phase of your new pricing with a select group of clients before a full-scale rollout. Monitor the performance, gather feedback, and be prepared to refine your strategy. It's common to revisit and adjust your pricing based on real-world feedback, underscoring the iterative nature of pricing strategy development.
Remember, the essence of value-based pricing lies in its focus on customer perception. It’s a strategy that not only seeks to understand what customers value but also aims to reflect that understanding in the pricing model, thereby fostering customer satisfaction and loyalty while optimizing revenue growth.
The key components of a buyer persona for value-based pricing include:
Personal background: This includes the persona's age, location, and other relevant demographic information.
Role in the company: Understanding the persona's job title, responsibilities, and decision-making authority is crucial for tailoring your product or service to their needs.
Pain points and challenges: Identifying the persona's pain points and challenges can help you create a product or service that addresses their specific needs and provides value.
Interests: Understanding the persona's interests and preferences can help you tailor your product or service to align with their values and priorities.
Habits: Analyzing the persona's habits, such as their preferred communication channels and purchasing patterns, can help you create a more personalized customer experience.
Budget: Determining the persona's budget constraints can help you set prices that are affordable and perceived as reasonable.
By understanding these key components, businesses can create detailed buyer personas that help them tailor their product or service to the needs and preferences of their target customers, ultimately leading to more effective value-based pricing strategies. Here are a couple of examples of user personas.
Quantifying a Buyer Persona
Quantifying a buyer persona in the context of SaaS pricing involves gathering detailed, data-driven insights about your target customers. This process includes:
Segmentation: Break down your customer base into distinct groups based on characteristics like industry, company size, and role within the company.
Data Collection: Utilize tools like ProfitWell or Clearbit to gather detailed demographic and behavioral data on current and potential customers.
Value and Price Sensitivity Analysis: Understand what features each persona values most and their willingness to pay for these features. Use techniques like relative preference analysis and Van Westendorp's Price Sensitivity Meter*.
Application to Pricing Strategy: Use the insights from quantified buyer personas to tailor your pricing strategy, ensuring that it aligns with what different customer segments value and are willing to pay.
*In Van Westendorp's Price Sensitivity Meter, four key questions are typically asked to gauge consumer price preferences:
This approach leads to a more targeted and effective pricing strategy, where pricing is optimized to match the perceived value of different customer segments.
In SaaS pricing strategy, quantified buyer personas are crucial. This approach emphasizes data-driven insights to deeply understand customers. By quantifying personas, product managers and marketers can accurately identify customer value, tailor pricing and packaging, enhance marketing and sales strategies, and guide product development. This data-centric methodology not only ensures pricing strategies are more effective but also boosts customer satisfaction and revenue growth.
Determining the Right Value Metric
In the context of SaaS, a value metric is a critical component for pricing strategies. It determines what aspect of the service is being charged for and directly relates to how customers derive value from the product. The right value metric is vital because:
It Aligns Pricing with Customer Value: By basing pricing on the value metric, companies ensure that the price reflects the value perceived by the customers.
Facilitates Customer Growth and Upselling: A well-chosen value metric grows with the customer. As customers' usage of the product increases, so does their payment, encouraging them to upgrade and use more of the service.
Improves Customer Satisfaction: When customers feel they are paying for the value they receive, it enhances satisfaction and loyalty.
Selecting the appropriate value metric, therefore, is a strategic decision that significantly impacts customer relationships, revenue growth, and market positioning for SaaS companies.
In case of Freshworks', the value metric in the provided pricing page is based on the level of functionality and support offered at each pricing tier. Typically, a value metric is a quantifiable feature that a SaaS company uses to differentiate its pricing plans. In this case, it could be the number of users, the extent of CRM automation, the depth of sales insights and analytics, or the degree of customization available. The more advanced the features and support, the higher the pricing tier, indicating that the value metric is tied to the complexity and comprehensiveness of the service provided.
Identifying and Leveraging Value Metrics
Identifying and leveraging value metrics is a critical step in implementing value-based pricing in a SaaS business. This involves understanding what aspects of your service are most valued by your customers and how these can be quantified and used as a basis for pricing. Here's an approach to this process:
1. Customer Segmentation and Analysis: Begin by segmenting your customer base into distinct groups based on their needs, usage patterns, and characteristics. Conduct thorough research to understand the specific needs and value perceptions of each segment.
2. Product Value Assessment: Evaluate your product's features and services to identify which elements deliver the most value to your customers. Consider conducting surveys, focus groups, or one-on-one interviews to gather customer feedback on what they value most about your product.
3. Determining the Value Metric: Choose a metric that reflects how customers derive value from your product. Common metrics in SaaS include per-user pricing, data usage, or feature-based pricing. Ensure that the chosen metric aligns with your customers' perception of value and encourages the desired usage behavior.
4. Pricing Model Development: Develop a pricing model that leverages the identified value metric. This model should differentiate between customer segments and reflect their varying willingness to pay. Consider creating tiered pricing plans that cater to different levels of usage or feature access, aligned with the value metric.
5. Communication Strategy: Develop a communication strategy that clearly articulates the value customers receive for the price they pay. Focus on marketing and sales efforts that highlight the benefits and outcomes associated with the product's features, as related to the value metric.
Transitioning to a value-based pricing model requires a deep understanding of your customers, a clear definition of your product's value, and a strategic approach to pricing. It involves not just setting the right prices but also aligning your entire business model and communications strategy around the value you deliver to your customers. Through this approach, SaaS companies can create more customer-centric pricing strategies that drive both revenue growth and customer satisfaction.
Who Should be on the Pricing Team?
The pricing committee in a SaaS organization should be a cross-functional team that includes representation from various departments to ensure a holistic approach to pricing. Here's a detailed breakdown of the roles and departments that should be included in the pricing committee:
Product Leadership: Members from the product team understand the features, benefits, and roadmap of the product, which is critical to setting a price that reflects its value.
Sales Leadership: Sales leaders bring insights into customer willingness to pay and the competitive landscape, as they are on the front lines interacting with prospects and customers.
Marketing Leadership: This group contributes valuable information on market positioning, buyer personas, and communication strategies for pricing changes.
Corporate Development/Finance: Finance professionals provide data on the company's financial performance and guide pricing strategies that align with overall business objectives.
Main Coordinator: Typically someone from the product or marketing department, this individual leads the pricing strategy project, coordinating efforts across departments.
Main Decision Maker: This is a senior-level executive, often the CEO or another C-suite member, who has the authority to make final decisions on pricing. Their involvement ensures that the pricing strategy aligns with the company’s vision and strategic goals.
The pricing committee works collaboratively to develop and refine the pricing strategy, taking into account customer value, competitive pricing, cost structure, and the company’s revenue goals. They are responsible for proposing pricing changes, testing pricing models, and analyzing the impact of pricing on customer acquisition and retention.
Brief Case Study of 3 SaaS Businesses on Transforming Value Perception Through Value-Based Pricing
Adobe Creative Cloud's Strategic Shift: Adobe revolutionized its revenue model by transitioning from traditional software licensing to a subscription-based model. This shift to value-based pricing mirrored the ongoing value delivered through regular updates and new features, leading to a substantial increase in Adobe's recurring revenue and enhanced customer engagement.
Salesforce CRM's Tiered Approach: Salesforce's CRM services exemplify value-based pricing with various service tiers, each offering an incremental increase in features and capabilities. This strategy effectively meets the diverse needs of different business sizes, solidifying Salesforce's position in the CRM market.
HubSpot's Scalable Solutions: HubSpot demonstrates value-based pricing with a range of service levels, from free basic tools to comprehensive enterprise solutions. This scalability allows customers to choose a plan that aligns with the value they require, fostering growth alongside their customers.
Each of these examples underscores the power of value-based pricing in the SaaS industry. By aligning pricing with customer-perceived value, these companies have not only maximized their revenue potential but also solidified lasting relationships with their customer base.
Common Challenges in Implementing Value-Based Pricing:
Understanding Customer Value Perception: One of the biggest challenges is accurately gauging how much customers value your product. Solution: Conduct in-depth market research, including surveys and customer interviews, to understand customer needs and how they perceive the value of your product.
Developing Buyer Personas: Creating detailed buyer personas can be complex. Solution: Utilize data analytics and customer feedback to create accurate personas that reflect the different segments of your market.
Determining the Right Value Metric: Choosing a value metric that aligns with customer perceived value is tricky. Solution: Evaluate different aspects of your product to find a metric that resonates with the majority of your customers, such as usage, features, or outcomes.
Communicating Value Effectively: Convincing customers of the value your product offers requires a strategic approach. Solution: Develop a comprehensive communication plan that clearly articulates the benefits and value of your product, supported by case studies and testimonials.
Adapting to Market Changes: The market is dynamic, and customer preferences can shift. Solution: Continuously monitor market trends and customer feedback to adapt your pricing strategy accordingly.
These challenges require a strategic approach and careful consideration, but when addressed effectively, they can significantly enhance the successful implementation of value-based pricing in your SaaS business.
The Future of Value-Based Pricing
The future of value-based pricing in SaaS is poised for transformative changes. Anticipated trends include a move towards more personalized and customized pricing structures tailored to individual customer value perceptions. The increasing use of data analytics will enable SaaS companies to refine their value propositions and dynamically adjust pricing. AI and machine learning integration will automate and optimize pricing strategies through predictive analytics. Additionally, a growing focus on customer success and outcomes will further align pricing with the tangible value delivered, reinforcing SaaS offerings' value proposition.
The Role of AI in Revolutionizing Pricing Strategies
Artificial Intelligence (AI) will continue to play a pivotal role in transforming pricing strategies. Let’s delve into how AI can enhance pricing processes and the necessary precautions for its implementation, drawing insights from comprehensive research.
AI's Augmentation in Pricing
Price Optimization: AI, particularly through machine learning, is instrumental in setting fair prices. It enables businesses to understand customer reactions to various pricing models and maximizes value across different market segments.
Data Analysis: The capability of AI to swiftly process complex data sets is invaluable. It supports value-based pricing, tiered pricing structures, and provides insights into customer's payment preferences.
Strategy Development: AI contributes significantly to the formulation of coherent global pricing strategies. It does so by amalgamating various data points such as historical sales, competitive analysis, and market trends.
Areas of Caution
Overreliance on AI: It’s imperative to understand that AI is a supportive tool and not a complete solution. Human oversight remains crucial in decision-making processes.
Strategic and Organizational Challenges: The integration of AI into pricing structures demands clear strategy, prioritization, and robust governance.
Data Management: Effective AI implementation in pricing strategies requires meticulous data collection, cleaning, normalization, and organization.
Trust and Transparency: Building trust in AI-driven recommendations and maintaining operational transparency is vital for their acceptance and effectiveness.
Long-Term Implementation: Embedding AI into an organization’s pricing strategy is an extensive process. It demands a solid foundation in both business strategy and data management.
AI offers tremendous potential in enhancing pricing strategies through sophisticated data analysis, strategic development, and optimization. However, its integration into business processes necessitates careful planning, strategic foresight, and an understanding that AI is a complement to, not a replacement for, human expertise. As businesses navigate through the complexities of pricing in a digital age, AI stands as a powerful ally, provided its application is approached with the necessary diligence and caution.
In conclusion, value-based pricing in the SaaS industry offers a customer-centric approach that prioritizes understanding and aligning with the perceived value of the product or service. By focusing on Positioning, Packaging, and Pricing as its core elements, businesses can tailor their pricing strategies to cater to diverse customer needs and enhance customer satisfaction. Unit economics, Buyer Personas, and Value Metrics are essential components that contribute to the successful implementation of value-based pricing. Case studies of industry leaders certainly demonstrate its effectiveness.
However, challenges such as grasping customer value perception and adapting to market changes underscore the importance of a cross-functional pricing team. Looking ahead, the future of value-based pricing in SaaS promises personalized pricing, data-driven insights, and AI integration. With careful consideration and a balanced approach, SaaS companies can continue to optimize their pricing strategies to foster growth, profitability, and customer success in this dynamic landscape.
Disclaimer: The views and insights expressed in this article are based on information gathered from various public sources on the internet and do not reflect any proprietary information belonging to the company where the author is currently employed or has worked in the past. The content is purely informative, intended for educational purposes, and not linked to any confidential or sensitive company data.